Mingsheng Aluminum Sheet Home > faq > Aluminum Alloy > Information on Japanese wayfinding signs
Information on Japanese wayfinding signs
Author:Aluminum Sheeting for Trailers_Aluminum Trailer Siding Sheets_Mingsheng Aluminum Update time:2025-04-24 08:13:012. Setting of intersection wayfinding signs
The wayfinding signs set up at intersections can be divided into three categories according to their relative positions and the functions they play: preview point signs (108 system), intersection signs (108 or 105 system), and confirmation point signs (106 system). Generally speaking, intersection signs are mandatory, but only at important intersections with high traffic volume and more than two lanes in one direction are teaser signs and confirmation signs installed. In Japan, intersections of general roads are provided according to the road class, traffic volume, and locality.
Intersection signs can be either location, direction and distance signs (105 system) or intersection signs (108 system) depending on the actual situation, but there is a big difference in the applicable conditions and characteristics of the two. In general, 105 system is applicable to road intersections with less than two lanes and unimportant road intersections, while 108 system is applicable to important road intersections with wider road width and larger traffic volume.
3. Information Selection of Signs
Information selection of signs is the most important work in the design of signs, which requires a comprehensive analysis of the urban layout, road network distribution, etc., to ensure that the guidance of signs meets the needs of traffic organisation. In China, the information of directional signs for highways outside the city is mainly based on the name of the area, and the information of directional signs for roads inside the city is mainly based on the name of the road, while in Japan, the information of directional signs is mainly based on the name of the area, and the roads mainly appear in the form of numbers.
(1) Classification of toponymic information
Toponymic information used as a route guide in Japan is classified into four main categories: (1) important places, (2) major places, (3) general places, and (4) benchmark places.
(2) Classification of General Roads
In Japan, general roads are classified according to their functional characteristics into: main arterial roads, arterial roads and auxiliary arterial roads, which is more similar to the classification of main roads, secondary roads and branch roads in China. The approximate classification is as follows:
① Main arterial roads: Skeleton roads connecting the metropolitan area and complementing motorways.
② Arterial roads: In addition to the main arterial roads, the main local roads, which play a complementary role to the main arterial roads.
③Auxiliary arterial roads: In addition to the main arterial roads. Trunk road outside the low-level roads, which plays a complementary role to the trunk road.
(3) Selection of Toponymic Information for Wayfinding Signs
In Japan, the design principle is to select the closest first-class toponymic information. In addition, for confirmation point signs, i.e., location and distance signs (106 system), in addition to those listed in the table, the reference place name should be selected in the top row of the sign. On major trunk roads, preview point and intersection signs of trunk roads (System 108), 2 place name information is usually displayed in the straight ahead direction, generally with the nearest first class place name information on the left and the nearest second class information on the right; however, if the 2 nearest locations are both first class place name information, the nearest first class place name information will be shown on the right, and the next nearest first class name information will be shown on the left. Here we take major arterial roads as an example to illustrate the main methods and principles for the selection of toponymic information for preview, intersection and confirmation point wayfinding signs. A set of wayfinding signs is set on National Highway 20, and the selection method of the toponymic information of the wayfinding signs is illustrated here with the direction of travelling straight ahead.
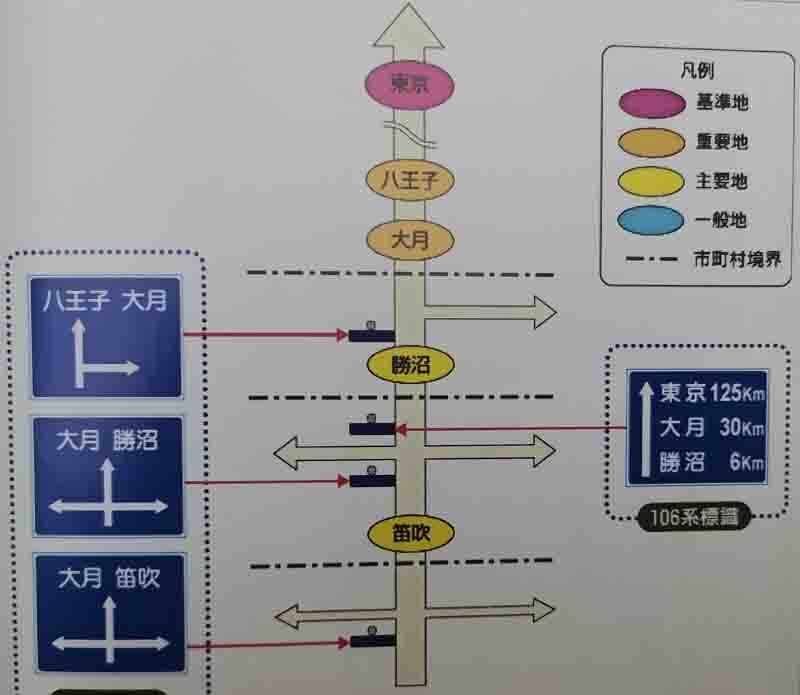
4. Text Size of Wayfinding Signs
(1) Size of Chinese Characters
In Japan, the size of Chinese characters for wayfinding signs is mainly considered according to the design speed of the road, and the width of the characters is equal to the height of the characters. For general roads, the height of the Chinese characters is usually 30cm; for motorways, the height of the Chinese characters is usually 50cm, taking into account the higher design speed.
(2) Size of English letters
Japanese road signs are in the form of Japanese and English, and the size of the English letters is based on the size of the Chinese characters. The height of uppercase English letters is 1/2 of the height of Chinese characters, and the height of lowercase English letters is 3/4 of the height of uppercase English letters.
(3) The size of sign face
The size of the sign face of the wayfinding sign is mainly decided according to the size of the text and the number of the text. However, standard specifications are used as far as possible in the case of conditions. Commonly used sign face specifications are: forecast point sign (length 280cm x width 240cm); intersection sign (length 280cm x width 220cm): confirmation point sign (length 240cm x width 200cm).
Article Categories
New Article
Contact Us
Contact:Maddy
Add:No. 162 Jinbai Road, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province, China
